A) frictional unemployment
B) the wage to rise above the equilibrium level
C) conflict between insiders who benefit from high union wages and outsiders who do not get the union jobs
D) reduced wages in industries without unions
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who of the following is not included in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' "employed" category?
A) those who worked in their own business
B) those who worked as unpaid workers in a family member's business
C) those waiting to be recalled to a job from which they had been laid off
D) those who were temporarily absent from work because of vacation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bureau of Labor Statistics is part of the U.S. Department of
A) the Treasury.
B) Commerce.
C) Labor.
D) the Interior.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Efficiency wages
A) increase frictional unemployment by keeping wages above equilibrium.
B) decrease frictional unemployment by keeping wages at equilibrium.
C) increase structural unemployment by keeping wages above equilibrium.
D) decrease structural unemployment by keeping wages at equilibrium.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) Unemployment insurance raises structural unemployment because it reduces the job search efforts of the unemployed.
B) Most economists are skeptical of the value of unemployment insurance primarily because they believe that it results in a poorer match between workers and jobs.
C) Studies show that when the unemployed become ineligible for benefits, the probability of their finding a job rises markedly.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Data on unemployment indicate that most people who become unemployed will soon find jobs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unpaid stay-at-home fathers are included in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' "unemployed" category.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If people who report being unemployed are not, in fact, trying hard to find a job, then the reported unemployment rate will be baised upward.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Workers searching for jobs that best suit them is most closely associated with
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) seasonal unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The process by which unions and firms agree on the terms of employment is called collective bargaining.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The demand for labor by a certain firm fluctuates as the demand for that firm's product fluctuates.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions
A) raise the wages of unionized workers and raise unemployment.
B) raise the wages of unionized workers and reduce unemployment.
C) reduce the wages of unionized workers and raise unemployment.
D) reduce the wages of unionized workers and reduce unemployment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Renee is the CEO of a corporation that hires nonunion labor. According to the theory of efficiency wages, if she decides to pay her workers more than the competitive equilibrium wage, then
A) the profits of her firm might increase.
B) the higher wages will induce her workers to shirk.
C) the turnover of her workers may increase.
D) she will face a shortage of labor.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Frictional unemployment is thought to explain
A) relatively short spells of unemployment, as is structural unemployment.
B) relatively long spells of unemployment, as is structural unemployment.
C) relatively short spells of unemployment, while structural unemployment is thought to explain relatively long spells of unemployment.
D) relatively long spells of unemployment, while structural unemployment is thought to explain relatively short spells of unemployment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The labor-force participation rate tells us the fraction of the population that
A) is able to participate in the labor market.
B) has ever been employed.
C) has chosen to participate in the labor market.
D) has chosen not to participate in the labor market.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a union raises the wage above the equilibrium level, it reduces the quantity of labor supplied and raises the quantity of labor demanded, resulting in unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Data show that at least 10 percent of U.S. manufacturing jobs are destroyed every year.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 10-4
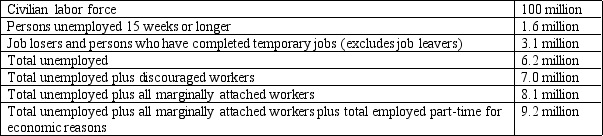 -Refer to Table 10-4. What is the U-3 measure of labor underutilization?
-Refer to Table 10-4. What is the U-3 measure of labor underutilization?
A) 4.7 percent
B) 6.2 percent
C) 7.0 percent
D) 10.9 percent
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who is not included in the labor force by the Bureau of Labor Statistics?
A) Calvin, who is on temporary layoff
B) Michael, who has retired and is not looking for work
C) Lauren, who does not have a job, but has applied for several in the last week
D) None of the above is correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to 2009 data on the U.S. population, which of the following groups of teenagers (ages 16-19) had the highest labor-force participation rate?
A) white males
B) white females
C) black males
D) black females
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 521 - 540 of 562
Related Exams